Unveiling the Iceman: Tattoos and Ancient Traditions
Unveiling the Iceman: Tattoos and Ancient Traditions
Introduction
"Hello everyone. I hope you're hydrated and having a wonderful day today," begins Gina, a professional tattoo artist with a keen interest in tattoo history. Exploring the fascinating discovery of Ötzi the Iceman, Gina uncovers how this 5,000-year-old mummified man, adorned with tattoos, has reshaped our understanding of ancient practices.
In this engaging exploration, we dive into the life and times of Ötzi, highlighting what his tattoos reveal about early human history and their enduring significance.
Finding Ötzi: A Discovery in the Alps
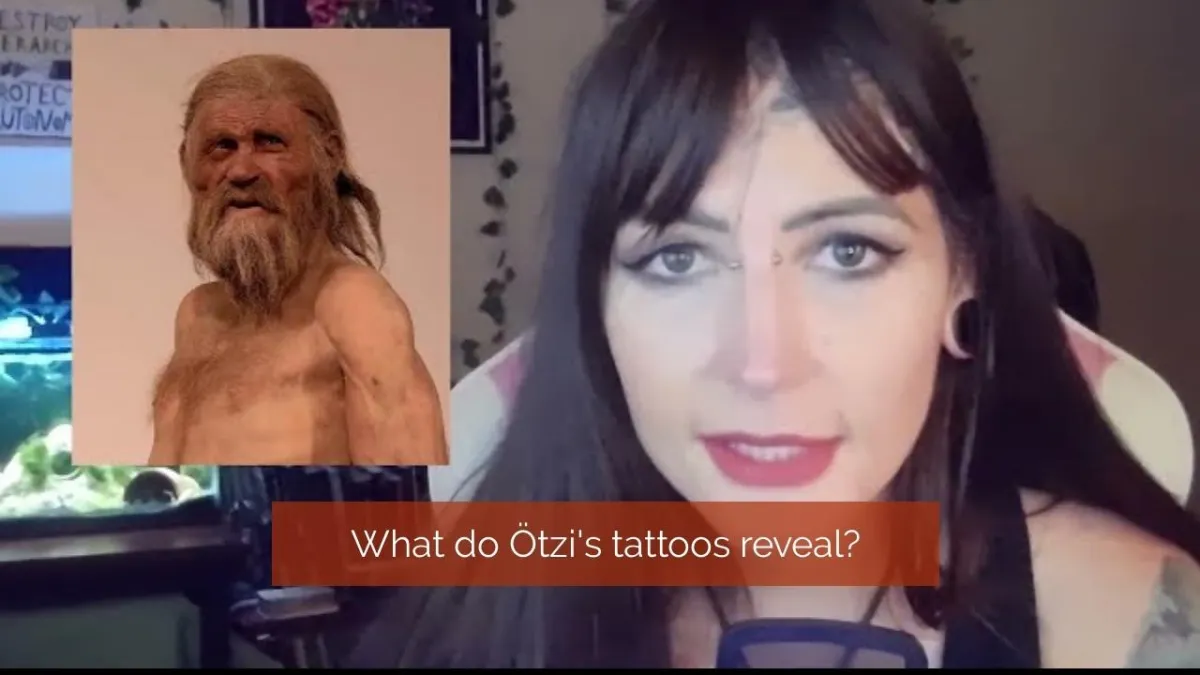
In 1991, hikers Erica and Helma Simon stumbled upon a mummified body in the Tisenyak Pass of the Ötztal Alps. Initially mistaken for a recent casualty, further investigation revealed Ötzi's age to be over 5,300 years old, dating back to the Copper Age.
Ötzi was discovered after an unusually hot summer melted parts of the glacier, exposing his mummified remains.
This accidental discovery has provided invaluable insights into prehistoric life, showing a time when society was transitioning into more complex, hierarchical structures.
A Glimpse into Ancient History
Ötzi was not a primitive caveman but part of a dynamic, interconnected world:
He was around 45 years old, of Anatolian farmer descent with a European hunter-gatherer ancestry mix.
His last meal included high-protein and carb-rich foods suitable for his active lifestyle.
The copper axe found with him suggests a position of status.
Ötzi's untimely death was likely due to an arrow wound and subsequent cranial trauma, implying a violent end.
The Mystery and Significance of Ötzi's Tattoos
One of the most compelling aspects of Ötzi's discovery is his tattoos.
Ötzi had 61 tattoos in 19 different clusters, primarily located on areas of chronic pain.
These tattoos represent the earliest known evidence of tattoo art, pre-dating acupuncture documentation in East Asia.
The likely use of tattooing aligns with ancient medicinal practices, suggesting a therapeutic purpose.
Current theories propose that these tattoos were applied via hand-poke methods, linking them to wider global tattoo traditions.
Major Impacts on Tattoo History
Ötzi's preserved tattoos offer profound insights into the universal nature of tattooing across cultures:
Global Tradition Evidence: Tattoos reflect a shared cultural and medicinal practice among ancient civilizations worldwide.
Deep Cultural Roots: For modern tattoo artists, Ötzi's legacy enriches the understanding of their craft, honoring its ancestral lineage.
Conclusion
The discovery of Ötzi the Iceman has dramatically shifted the narrative of tattoo history, illustrating their role not only as art but as a means of healing. For tattoo business owners, recognizing this rich heritage can foster deeper connections with clients and enhance appreciation for the profession.
Gina expresses her enthusiasm for sharing this intriguing history, inviting audience engagement and further exploration into the ancient world of tattoos. "I hope you've enjoyed this journey into the past," she concludes warmly, encouraging feedback and suggestions for future discussions.

